"USAspending.gov, available at http://www.USAspending.gov, is a government source for data on
federal awards by state, congressional district (CD), county, city, and zip code. The awards data in
USAspending.gov are provided by federal agencies and represent contracts, grants, loans, and
other forms of financial assistance. USAspending.gov also provides tools for examining the
broader picture of federal spending obligations within the categories of budget function, agency,
and object class.
Using USAspending.gov to locate and compile accurate data on federal awards can be
challenging due, in part, to continuing data quality issues that have been identified by the U.S.
Government Accountability Office (GAO). Users of USAspending.gov need to be aware that
while search results may be useful for informing consideration of certain questions, these results
may be incomplete or contain inaccuracies.
USAspending.gov was created under P.L. 109-282, the Federal Funding Accountability and
Transparency Act of 2006 (FFATA), and later enhanced under requirements in P.L. 113-101, the
Digital Accountability and Transparency Act of 2014 (DATA Act).
Other federal awards data sources reviewed in this report include the following:
Federal Procurement Data System (FPDS);
Census Federal Audit Clearinghouse;
U.S. Budget: Aid to State and Local Governments;
Rockefeller Institute of Government;
Federal Funds Information for States;
Census Federal Aid to States (FAS) and Consolidated Federal Funds
Report (CFFR); and
Additional federal grant awards database.."
Federal Awards
Friday, April 29, 2022
Tracking Federal Awards: USAspending.gov and Other Data Sources
Tuesday, April 26, 2022
Arms Control and Nonproliferation: A Catalog of Treaties and Agreements
"Arms control and nonproliferation efforts are two of the tools that the United States has
occasionally used to implement its national security strategy. Although some believe these tools
do little to restrain the behavior of U.S. adversaries, while doing too much to restrain U.S.
military forces and operations, many others see them as an effective means to promote
transparency, ease military planning, limit forces, and protect against uncertainty and surprise.
Arms control and nonproliferation efforts have produced formal treaties and agreements, informal
arrangements, and cooperative threat reduction and monitoring mechanisms. After the end of the
Cold War, the pace of implementation for many of these agreements slowed during the Clinton
Administration. The Bush Administration usually preferred unilateral or ad hoc measures to
formal treaties and agreements to address U.S. security concerns. The Obama Administration
resumed bilateral negotiations with Russia and pledged its support for a number of multilateral
arms control and nonproliferation efforts, but succeeded in negotiating only a few of its priority
agreements. The Trump Administration withdrew the United States from the INF Treaty and the
Open Skies Treaty. It did not support the full five-year extension of the New START Treaty but
did seek to negotiate a short-term extension during the latter half of 2020. These talks failed to
produce an agreement. It also advocated discussions on a future treaty that would limit all types
of U.S., Russian, and Chinese nuclear weapons, but most arms control analysts doubt that China
would participate in this process. The Biden Administration supported the full five-year extension
of New START and reached an agreement with Russia that took effect on February 3, 2021.
The United States and Soviet Union began to sign agreements limiting their strategic offensive
nuclear weapons in the early 1970s. Progress in negotiating and implementing these agreements
was often slow, and subject to the tenor of the broader U.S.-Soviet relationship. As the Cold War
drew to a close in the late 1980s, the pace of negotiations quickened, with the two sides signing
treaties limiting intermediate-range and long-range weapons. But progress again slowed in the
1990s, as U.S. missile defense plans and a range of other policy conflicts intervened in the U.S.-
Russian relationship. At the same time, however, the two sides began to cooperate on securing
and eliminating Soviet-era nuclear, chemical, and biological weapons. Through these efforts, the
United States has allocated more than $1 billion each year to threat reduction programs in the
former Soviet Union. These programs have recently reached their conclusion.
The United States is also a prominent actor in an international regime that attempts to limit the
spread of nuclear weapons. This regime, although suffering from some setbacks in recent years in
Iran and North Korea, includes formal treaties, export control coordination and enforcement,
U.N. resolutions, and organizational controls. The Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT) serves
as the cornerstone of this regime, with all but four nations participating in it. The International
Atomic Energy Agency not only monitors nuclear programs to make sure they remain peaceful,
but also helps nations develop and advance those programs. Other measures, such as sanctions,
interdiction efforts, and informal cooperative endeavors, also seek to slow or stop the spread of
nuclear materials and weapons.."
Arms control
Saturday, April 23, 2022
Digital Wallets and Selected Policy Issues
"Digital Wallet Landscape
A digital wallet is a software application that stores
payment or account details to facilitate traditional payments
that use bank and credit card details and/or cryptocurrency
transactions. In addition, wallets facilitate peer-to-peer
transfers, which have grown rapidly in recent years (Figure
1). This In Focus discusses three types of digital wallets and
addresses selected policy issues.
Functionality and Scope of Use
Digital wallets are generally used for (1) payments to
merchants through the use of near-field communication or
QR codes for in-person purchases; (2) peer-to-peer transfers
of funds through an app, via text message, or QR codes; (3)
storing value from a linked bank account or debit card on
an app-based account; or (4) storing, providing access to,
and transacting in cryptocurrency. (For more on
cryptocurrency, see CRS Report R45427, Cryptocurrency:
The Economics of Money and Selected Policy Issues.)
Digital wallets generally require the use of internet connected hardware, such as a smartphone. Some, including
Apple Pay and Google Pay, may work only with certain
devices and associated operating systems. Others, such as
the PayPal or Cash apps, can be downloaded and accessed
from a range of devices, irrespective of operating system.
For conceptual simplicity, it can be helpful to think of
digital wallets as belonging to one of three groups: retailer specific, general purpose, or cryptocurrency.
Retailer-specific mobile wallets are offered by a retailer for
use to purchase its goods and services. They allow
individuals to store payment card information, upload funds
to digital or registered gift cards, or prefund a balance on an
app for future transactions..."
Digital wallets
Growing Jobs in Environmentally Focused Occupations
"If your career plan involves caring for the planet, there’s good news. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects job growth in many occupations related to helping the environment or conserving natural resources.
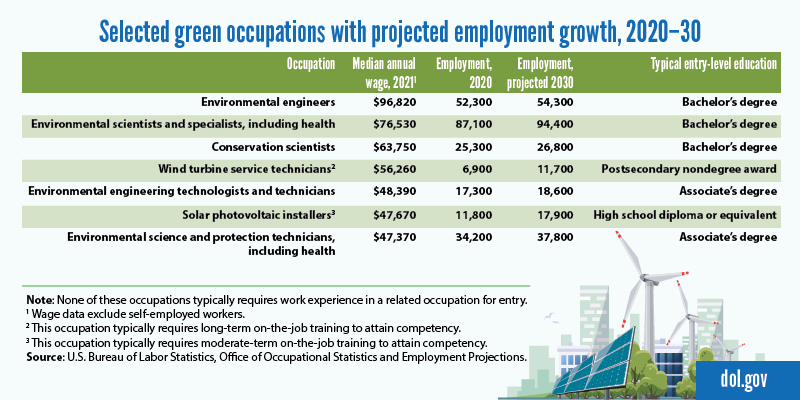
In fact, two of the occupations that BLS projects to have the fastest employment growth from 2020 to 2030, wind turbine service technicians (68% increase) and solar photovoltaic installers (52% increase), involve “green” work. However, as the data show, the total number of new jobs is projected to be relatively small in these and some other green occupations.
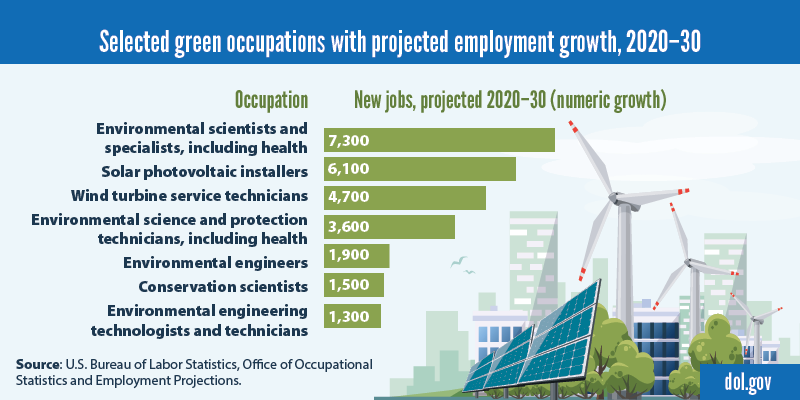
Each of these occupations had a median annual wage that was higher than the $45,760 median for all workers in 2021. The typical education required to enter these occupations varies.
Workers in green occupations focus on the environment in different ways. Wind turbine service technicians and solar photovoltaic installers, for example, build and maintain systems that create energy from sources that don’t become depleted. Other workers help to monitor the environment and investigate sources of pollution. Still others advise organizations or individuals on ways to protect and preserve natural resources.
Opioid Overdose Prevention
"Substance use disorders, like opioid use disorder (OUD), have significantly impacted communities across America. When we act early, we can prevent the use and misuse of drugs, like opioids, that can lead to substance use disorders. Prevention activities work to educate and support individuals, families, and communities and are critical for maintaining both individual and community health.
Opioid use disorder and overdoses are preventable
Opioid Use Disorder (OUD), sometimes referred to as “opioid abuse or dependence” or “opioid addiction,” is a problematic pattern of opioid use that causes significant impairment or distress. OUD is a medical condition that can affect anyone – regardless of race, gender, income level, or social class. Like many other medical conditions, there are evidence-based treatments that are available for OUD, but seeking treatment remains stigmatized. Stigma can be a major barrier to how well prevention and treatment programs can work to address the opioid crisis.
Stigma or the fear of stigma may stop someone from sharing their health condition with partners or family members. It may also prevent them from accessing seeking the health or behavioral health services and support services they need. People who experience health-related stigma may also experience less access to healthcare, delayed diagnosis of a condition, and reduced adherence to treatments. Learn more about what you can do to reduce stigma and support recovery.
OUD significantly contributes to overdose deaths among people who use illicit opioids or misuse prescription opioids. Opioids—mainly synthetic opioids like illicitly manufactured fentanyl (other than methadone)—are currently the main cause of drug overdose deaths. For every drug overdose that results in death, there are many more nonfatal overdoses, each one with its own emotional and economic toll. OUD and overdose deaths continue to be a major public health concern in the United States, but they are preventable.."
Opioids
Monday, April 18, 2022
Food Delivery Safety
"Mail-order food, subscription meal kits, home-delivered groceries, and restaurant deliveries can be convenient. Make sure food safety is part of the package, too. Home-delivered food, like all food, must be handled properly to prevent food poisoning.
Handling delivered food safely is important for everyone, but especially if you are buying food for someone who is more likely to get food poisoning:
- adults aged 65 and older,
- children younger than age 5,
- people who have health problems or take medicines that lower the body’s ability to fight germs and sickness (weakened immune system), and
- pregnant people.
Meal Kits and Other Shipped Food
Food shipped to your home needs to stay at a safe temperature to prevent the growth of germs that could make you sick. This includes mail-order food and subscription meal kits.
Before Ordering Food for Delivery
Ask questions first. Research companies and call customer service to ask about food safety practices.
Ask how the company responds if food is delivered at an unsafe temperature or is otherwise not safe to eat. Find out if the company provides information with each shipment or delivery on safe handling and preparation of food, including cooking temperatures.
Safe Food Delivery and Receipt
Arrange for delivery when someone is at home so perishable foods such as meat, seafood, poultry, eggs, or dairy can be quickly stored in the refrigerator or freezer instead of being left outside until someone is home. If you can’t be there in person, see if a neighbor can store the food until you return.
Find a safe space for delivery if no one can be at home when food arrives. Food should be delivered to a cool, shaded, and secure location where pests and rodents won’t be able to get it. Let the company know where you would like them to leave your box.
Examine the items and packaging to ensure they are intact.
- Make sure the company used insulated packaging and materials such as dry ice or frozen gel packs to keep perishable food cold in transit.
- Look for labels that say “Keep Refrigerated” or “Keep Frozen” if you ordered perishable food.
Use a food thermometer to check the temperature of perishable food when it arrives.
- Perishable food that has been shipped should arrive frozen, partially frozen with ice crystals still visible, or at least as cold as it would be in a refrigerator (40°F or below). Even if a perishable food product is smoked, cured, vacuum-packed, or fully cooked, it still must be kept cold.
Store perishable food at a safe temperature. After you make sure perishable food was delivered at a safe temperature (40°F or below), store it in the refrigerator or freezer as soon as possible until you are ready to prepare it.
Notify the company if food arrives above 40°F. If food arrives above 40°F, don’t eat it, or even taste it, to see if it is safe. Food can be unsafe and still taste, look, and smell OK. When in doubt, throw it out..."
Food delivery
Thursday, April 14, 2022
United States Life Tables, 2019
"Abstract
Objectives—This report presents complete period life tables
for the United States by Hispanic origin, race, and sex, based on
age-specific death rates in 2019. Starting with the 2019 data year,
this report adds life tables for the non-Hispanic American Indian
or Alaska Native (AIAN) and non-Hispanic Asian populations.
Methods—Data used to prepare the 2019 life tables are
2019 final mortality statistics; July 1, 2019, population estimates
based on the 2010 decennial census; and 2019 Medicare data
for people aged 66–99. The methodology used to estimate the
life tables for the Hispanic population remains unchanged from
that developed for the publication of life tables by Hispanic origin
for data year 2006. The same methodology is used to estimate
the life tables for the non-Hispanic AIAN and non-Hispanic Asian
populations. The methodology used to estimate the 2019 life
tables for all other groups was first implemented with data year
2008.
Results—In 2019, the overall expectation of life at birth was
78.8 years, increasing from 78.7 in 2018. Between 2018 and
2019, life expectancy at birth increased by 0.1 year for males
(76.2 to 76.3) and by 0.2 year for females (81.2 to 81.4). In 2019,
life expectancy at birth was 85.6 years for the non-Hispanic Asian
population, 81.9 years for the Hispanic population, 78.8 years
for the non-Hispanic White population, 74.8 years for the nonHispanic Black population, and 71.8 years for the non-Hispanic
AIAN population. Between 2018 and 2019, life expectancy
increased 0.2 year for the non-Hispanic White population and
by 0.1 year for the Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black populations..."
Life tables
Census Bureau Releases New U.S. Population Estimates by Age and Sex
"APRIL 14, 2022 — The U.S. Census Bureau today released a downloadable file containing estimates of the nation’s resident population by sex and single year of age for July 1, 2021. It is available at <www.census.gov/programs-surveys/popest.html>.
In the coming months, the Census Bureau will release additional population estimates for cities and towns, as well as national, state and county population estimates by age, sex, race and Hispanic origin..."
Population by age and sex
Tuesday, April 12, 2022
New Report on Undercount of Young Children in 2020 Census and Comparison to 2010
[The Census Project]
"A new report on the undercount of young children in the 2020 Census also provides a comparison between 2010 and 2020 Census efforts in counting young children. It “provides an overview of the research and new activities related to the net undercount of young children that occurred as planning for the 2020 Census began,” including “a review of new activity within the Census Bureau, mobilization of researchers and advocates on this issue outside the Census Bureau, and how the Census Bureau and the child advocacy community worked together on this problem.”
The report focuses “on the net undercount of young children in recent U.S. Censuses,” but notes that the “issue is bigger than the 2010 U.S. Census. Over the past 70 years, the U.S. Census has seen a consistently high net undercount of young children and there is an under-reporting of young children in major Census Bureau surveys…. Young children have high net undercounts in many other countries around the world…. In other words, this problem exists in many different cultures with different census-taking traditions. Despite changes in the U.S. Census Bureau methods over the past 70 years, as well as fundamental changes in U.S. society, the undercount of young children has remained high.”
- “Counting Young Children in the U.S. Census – Important Differences Between 2010 and 2020.” by Deborah H. Griffin and William P. O’Hare. March 29, 2022. https://civilrightsdocs.info/pdf/reports/Counting-Young-Children-in-the-Census-Report.pdf.."
Children Census undercount
Blockchain: Novel Provenance Applications
"Blockchain, generally, is a database technology that records and stores information in blocks of
data that are linked, or “chained,” together. Data stored on a blockchain are continually shared,
replicated, and synchronized across the nodes in a network—individual computer systems or
specialized hardware that communicate with each other and store and process information. This
system enables tamper-resistant record keeping without a centralized authority or intermediary.
There are multiple types of blockchains, and, depending on the type, recorded data may be
accessible to all users or only a designated subset. All blockchains share common characteristics,
including decentralization (i.e., no centralized authority), immutability (i.e., the blockchain records are unalterable), and
pseudonymity (i.e., how users’ real-world identities are handled). Certain blockchain types may offer greater levels of
decentralization and pseudonymity than others. New blockchain applications, such as smart contracts, non-fungible tokens,
and decentralization autonomous organizations, may automate processes or replace intermediaries in a variety of fields.
Recent developments in blockchain governance protocols and consensus mechanisms have raised concerns about the
environmental impact, oversight, and accountability of blockchain networks.
Since its creation in 2008, blockchain has been most commonly associated with cryptocurrencies—digital currencies that
users exchange through decentralized computer networks. More recently, public and private sector actors have used
blockchain applications in fields such as supply chain management, identity management, and asset registration. Blockchain
technologies may enable establishing the provenance of goods and tracking their progression through a supply chain;
identity-management with digital credentials; recording the ownership of digital and physical objects; and the transfer of
property, rights, or goods without a third-party intermediary. The United States is a hub for private-sector blockchain
development, and many states and federal agencies are experimenting with novel blockchain provenance applications,
including the Food and Drug Administration and Department of Treasury..."
Blockchain
Saturday, April 9, 2022
Articles of Agreement Relating to the Surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia
"On April 9, 1865, Generals Ulysses S. Grant and Robert E. Lee met in the parlor of a house in Appomattox Court House, VA, to discuss this surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia, which would end the Civil War. According to the terms, the men of Lee's army could return home in safety if they pledged to end the fighting and deliver their arms to the Union Army.."
Lee's surrender
Thursday, April 7, 2022
A Code of Conduct for the Supreme Court? Legal Questions and Considerations
"The Code of Conduct for United States Judges (the Code) is a set of ethical canons that the JudicialConference of the United States (Judicial Conference) has adopted to promote public confidence in the
integrity, independence, and impartiality of the federal judiciary. The Code governs the behavior of most
federal judges; however, it does not explicitly apply to Justices of the U.S. Supreme Court. Although the
Justices consult the Code, along with other sources, for guidance when performing their judicial duties,
the Court is not presently subject to a defined body of general ethical rules.
Some observers maintain that “Supreme Court justices should be bound by the same code of ethics that
all other federal judges are required to follow.” To that end, some Members of Congress have introduced
legislation that would require the Judicial Conference to “issue a code of conduct[] which applies to each
justice” on the Court. While some commentators and legislators have supported ethical rules for the
Supreme Court for years, the issue gained increased prominence in March 2022 following reports that
Virginia Thomas, wife of Associate Justice Clarence Thomas, sent text messages in January 2021 to thenWhite House Chief of Staff Mark Meadows encouraging him to contest the result of the 2020 presidential
election. In response to those reports, some have debated whether Justice Thomas should recuse himself
from certain cases voluntarily, while others have called for broader changes to the Court’s ethical
obligations that would bind all the Justices. By contrast, some commentators question whether Congress
should—or even could—impose a code of ethics on the Supreme Court.
This Sidebar canvasses the relevant legal considerations surrounding proposals to establish a Supreme
Court code of conduct. After discussing the existing Code that applies to lower federal judges, the Sidebar
describes recent legislative proposals to create a similar code for the Supreme Court, as well as potential
constitutional obstacles to those proposals..."
Supreme Court code of conduct
Wednesday, April 6, 2022
War Crimes: A Primer
"The Russian invasion of Ukraine has given rise to numerous accusations of war crimes. This Legal
Sidebar addresses the sources and content of the law of war, also known as the law of armed conflict or
international humanitarian law (IHL) as it pertains to war crimes that occur in an international armed
conflict. IHL applies to the conduct of war; it does not address the legality of the war itself. For
information about potential accountability for war crimes in international tribunals, see CRS Legal
Sidebar LSB10704, The Role of International Tribunals in the Response to the Invasion of Ukraine, by
Nina M. Hart and Stephen P. Mulligan.
Sources of International Humanitarian Law
IHL is a combination of international treaties and customary international law. The Hague Convention of1907 generally prescribes rules of conduct for armed forces, while the Geneva Conventions and Protocol
Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949, and relating to the Protection of Victims of
International Armed Conflicts 1 (Protocol 1) address the rights of protected persons, such as civilians and
prisoners of war, in an international armed conflict. Not all states are parties to these and other treaties
pertaining to the law of war, but many provisions are regarded as reflecting customary international law,
which is binding on all states.
Principles of International Humanitarian Law.
Certain principles undergird IHL and form the basis for the content of war crimes and serve to reduce
unnecessary suffering during war. The most important principles are military necessity, humanity, and
honor. The principles of distinction and proportionality flow from the first three. The Department of
Defense’s Law of War Manual describes their interaction as follows:
Military necessity justifies certain actions necessary to defeat the enemy as quickly and efficiently
as possible. Conversely, humanity forbids actions unnecessary to achieve that object.
Proportionality requires that even when actions may be justified by military necessity, such actions
not be unreasonable or excessive. Distinction underpins the parties’ responsibility to comport their
behavior with military necessity, humanity, and proportionality by requiring parties to a conflict to
apply certain legal categories, principally the distinction between the armed forces and the civilian
population. Lastly, honor supports the entire system and gives parties confidence in it. (Citations
omitted).
The main purposes of the law of armed conflict are:
Protecting combatants, noncombatants, and civilians from unnecessary suffering;
Providing certain fundamental protections for persons who fall into the hands of the
enemy, particularly prisoners of war, military wounded and sick, and civilians;
Facilitating the restoration of peace;
Assisting the commander in ensuring the disciplined, ethical, and effective use of military
force;
Preserving the professionalism and humanity of combatants; and
Preventing the degeneration of warfare into savagery or brutality.."
War crimes
IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
[Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change]
"The evidence is clear: the time for action is now. We can halve emissions by 2030.
GENEVA, Apr 4 – In 2010-2019 average annual global greenhouse gas emissions were at their highest levels in human history, but the rate of growth has slowed. Without immediate and deep emissions reductions across all sectors, limiting global warming to 1.5°C is beyond reach. However, there is increasing evidence of climate action, said scientists in the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report released today.
Since 2010, there have been sustained decreases of up to 85% in the costs of solar and wind energy, and batteries. An increasing range of policies and laws have enhanced energy efficiency, reduced rates of deforestation and accelerated the deployment of renewable energy.
“We are at a crossroads. The decisions we make now can secure a liveable future. We have the tools and know-how required to limit warming,” said IPCC Chair Hoesung Lee. “I am encouraged by climate action being taken in many countries. There are policies, regulations and market instruments that are proving effective. If these are scaled up and applied more widely and equitably, they can support deep emissions reductions and stimulate innovation.”
The Summary for Policymakers of the IPCC Working Group III report, Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of climate change was approved on April 4 2022, by 195 member governments of the IPCC, through a virtual approval session that started on March 21. It is the third instalment of the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), which will be completed this year..."
Climate Assessment Report
Past, Present, and Future Impact of SEED
"CDC recognizes April as Autism Acceptance Month. We are highlighting the work we’ve done through CDC’s Study to Explore Early Development (SEED) and what we’ve learned about autism spectrum disorder (ASD) so far. Join the nationwide effort to raise awareness and promote acceptance of ASD and its impact on children and families.
CDC’s Study to Explore Early Development (SEED) is the largest study in the United States to help us learn more about autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in preschool-aged children, including risk factors and what signs to look for. SEED has now been expanded to learn more about the health, functioning, and needs of children with ASD and other developmental disabilities as they mature.
What Have We Learned from CDC’s Study to Explore Early Development (SEED) So Far?
- There is not one cause of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). There are several factors associated with the development of ASD, including
- Mother and child autoimmune conditions, such as eczema/psoriasis,
- Pregnancy factors, such as infection with fever in the second trimester of pregnancy, and
- Environmental factors, such as the interaction between air pollution and neighborhoods with high poverty.
- Children with ASD are more likely to have developmental delays, gastrointestinal issues, and sleep problems, and to engage in self-harming behaviors.
- Contrary to recommendations, many children with ASD are given medication to treat challenging behaviors before they receive behavior therapies.
- Adolescents with ASD are much more likely to have mental health conditions and unmet health care needs.."
SEED
Five Facts About Davis-Bacon and Related Acts
"With President Biden’s signing of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law on Nov. 15, 2021, our nation is poised to address our aging infrastructure and at the same time create an estimated 800,000 good paying jobs in construction and related industries. Most of the construction projects funded or assisted through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law will be subject to Davis-Bacon prevailing wage labor standards. That means construction workers on these projects must be paid at least the locally prevailing wage and fringe benefits required for the work they perform...
Davis-Bacon is a federal law that requires local prevailing wages be paid on most federal and federally funded construction contracts. The Davis-Bacon Act ensures that federal government funds elevate labor standards for construction workers across the country, and that taxpayer dollars are used to ensure local wage and benefit standards, allowing responsible contractors to compete for federally funded or assisted construction contracts.
If it’s a Davis-Bacon project, it requires Davis-Bacon wages. Construction workers working on Davis-Bacon covered construction contracts must be paid no less than the locally prevailing wages for all hours worked in each labor classification. If a construction worker on a Davis-Bacon project works in more than one labor classification, the contractor or subcontractor must pay the highest applicable wage rate for all hours worked or different wage rates based on the actual hours worked in each labor classification. Local wage determinations that list labor classification and wage rates are issued by the Wage and Hour Division of the U.S. Department and can be found at sam.gov.
Understand the wages owed to construction workers. Contractors and subcontractors on Davis-Bacon projects must pay their construction workers not less than the wages and fringe benefits listed on the wage determination for the work performed. To help ensure workers are paid the proper rates, workers, contractors and subcontractors should familiarize themselves with:
where the work is being performed,
the type of construction (building, residential, highway, or heavy), and
the applicable labor classifications for the work being performed..."
Davis-Bacon Act
Friday, April 1, 2022
1950 Census Records
"On April 1, 2022, the 1950 Census records were released and are available free of charge.
Search the 1950 Census at 1950Census.Archives.gov
Taken every 10 years since 1790, the United States census provides a snapshot of the nation's population. Because of a 72-year restriction on access to the records, the most recent census year currently available is 1950.
On April 1, 2022, the 1950 Census was released, and users can access it for free through a dedicated website at 1950census.archives.gov. This population census is the 17th decennial census of the United States. The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) has digitized and is providing free online access to the 1950 Census population schedules for U.S. states and territories, enumeration district maps, and enumeration district descriptions.
Bulk Download: In addition, researchers can download the full 1950 Census dataset through the Amazon Web Services' (AWS) Registry of Open Data .
How You Can Help
You can search the 1950 Census website by name and location. You can also search by Indian Reservation for form P8 Indian Reservation Schedules.
To develop the initial name index, we are using Amazon Web Services’ artificial intelligence / optical character recognition (AI/OCR) Textract tool to extract the handwritten names from the digitized 1950 Census population schedules.
Because the initial name index is built on optical character recognition (OCR) technology, it is not 100-percent accurate. The National Archives is asking for your help in submitting name updates to the index using a transcription tool that is available on the 1950 Census website. You can help us improve the accuracy of the name index and make the records more accessible for everyone. More information will be forthcoming.."
1950 Census
 .."
.."