"Impetigo (im-peh-TIE-go) is a bacterial infection of the skin that is most common in young children. Doctors use antibiotics to treat impetigo. Antibiotics can also help protect others from getting sick.
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by one or both of the following bacteria: group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus. This page focuses on impetigo caused by group A Streptococcus (group A strep). In addition to impetigo, group A strep cause many other types of infections.
How Someone Gets Impetigo
When group A strep infects the skin, it causes sores. The bacteria can spread to others if someone touches those sores or comes into contact with fluid from the sores.
Signs and Symptoms
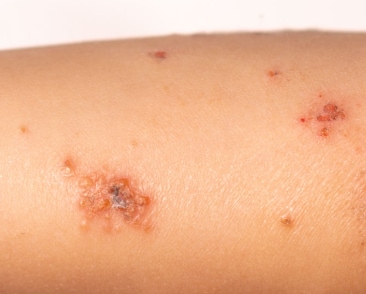
Impetigo starts as a red, itchy sore. As it heals, a crusty, yellow or “honey-colored” scab forms over the sore.
In general, impetigo is a mild infection that can occur anywhere on the body. It most often affects exposed skin, such as around the nose and mouth or on the arms or legs.
Symptoms include red, itchy sores that break open and leak a clear fluid or pus for a few days. Next, a crusty yellow or “honey-colored” scab forms over the sore, which then heals without leaving a scar.
It usually takes 10 days for sores to appear after someone is exposed to group A strep.
Young Children Are at Increased Risk
Anyone can get impetigo, but some factors increase someone’s risk of getting this infection.
- Age: Impetigo is most common in children 2 through 5 years old.
- Infections or injuries that break the skin: People with scabies infection are at increased risk for impetigo. Participating in activities where cuts or scrapes are common can also increase someone’s risk of impetigo.
- Close contact or crowding: Close contact with another person with impetigo is the most common risk factor for illness. For example, if someone has impetigo, it often spreads to other people in their household. Infectious illnesses also tend to spread wherever large groups of people gather. Crowded conditions — such as those in schools and daycare centers — can increase the spread of impetigo.
- Climate: Impetigo is more common in areas with hot, humid summers and mild winters (subtropics), or wet and dry seasons (tropics), but it can occur anywhere.
- Poor personal hygiene: Lack of proper handwashing, body washing, and facial cleanliness can increase someone’s risk of getting impetigo..."
Impetigo
No comments:
Post a Comment